Zero Trust Security Model: Rethinking Cybersecurity for Modern Organizations
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, traditional cybersecurity models are increasingly inadequate. With the rise of remote work, cloud computing, and sophisticated cyber threats, organizations must rethink their security strategies. The Zero Trust Security Model has emerged as a revolutionary approach, fundamentally shifting how businesses protect their data and systems. This article explores the principles of the Zero Trust model, its benefits, and how organizations can implement it effectively.
Understanding the Zero Trust Security Model
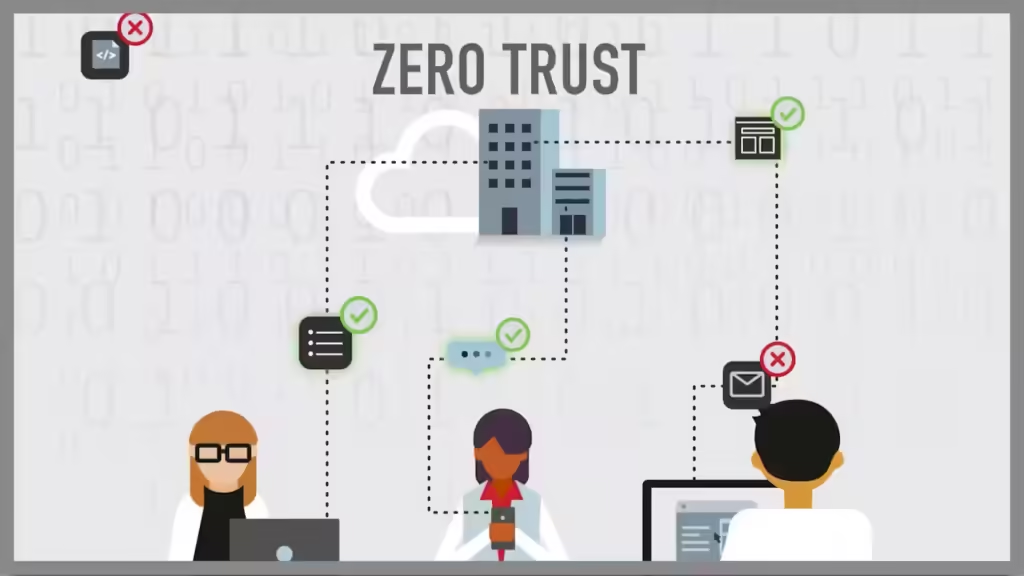
The Zero Trust Security Model is based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security models that assume trust based on network location, Zero Trust operates on the premise that threats can exist both inside and outside the network perimeter. Therefore, every access request must be verified, regardless of whether the user is within the organization’s firewall or connecting remotely.
Core Principles of Zero Trust
- Least Privilege Access: Users and devices are granted only the permissions necessary to perform their specific functions. This minimizes the potential damage from compromised accounts.
- Continuous Verification: Access requests are subject to ongoing validation, ensuring that users and devices are authenticated before being granted access to resources.
- Micro-Segmentation: The network is divided into smaller, isolated segments to limit lateral movement by attackers. This containment strategy ensures that even if one segment is compromised, the entire network remains secure.
- Assume Breach: Organizations operate under the assumption that a breach could occur at any time. This mindset encourages proactive security measures, including robust monitoring and incident response plans.
Benefits of the Zero Trust Model
1. Enhanced Security Posture
By continuously verifying access and enforcing the principle of least privilege, organizations significantly reduce their attack surface. This proactive approach makes it more challenging for cybercriminals to gain access to sensitive information.
2. Improved Data Protection
Zero Trust models prioritize data security, ensuring that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized users. By implementing encryption and data loss prevention measures, organizations can further safeguard their critical assets.
3. Support for Remote Work
As remote work becomes the norm, traditional perimeter-based security models fall short. Zero Trust accommodates a distributed workforce by securing access to resources regardless of the user’s location, ensuring a seamless and secure experience.
4. Regulatory Compliance
With stringent regulations surrounding data protection, such as GDPR and HIPAA, organizations must implement comprehensive security measures. The Zero Trust model’s focus on access control and data security can help businesses meet compliance requirements more effectively.
Implementing a Zero Trust Security Model
To transition to a Zero Trust Security Model, organizations should follow these steps:
1. Assess Current Security Posture
Conduct a thorough assessment of existing security measures, identifying vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. Understanding the current landscape will help inform the Zero Trust implementation strategy.
2. Define User and Device Identities
Establish clear identities for users and devices, employing multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance verification processes. This step ensures that only authorized individuals and trusted devices can access critical resources.
3. Implement Micro-Segmentation
Segment the network to limit access to sensitive information. By isolating critical resources, organizations can contain potential breaches and prevent lateral movement within the network.
4. Monitor and Analyze Activity
Continuous monitoring is essential in a Zero Trust environment. Employ advanced analytics and threat detection tools to identify suspicious behavior and respond promptly to potential threats.
5. Educate Employees
Employee awareness is critical in any cybersecurity strategy. Provide training on Zero Trust principles, emphasizing the importance of vigilance and adherence to security protocols.
Conclusion
The Zero Trust Security Model represents a paradigm shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity. By moving away from the outdated notion of trusted networks, businesses can better protect their sensitive data and systems against a myriad of threats. As cybercriminals become increasingly sophisticated, adopting a Zero Trust model is not just an option—it is a necessity for modern organizations committed to safeguarding their digital assets. By implementing the principles of Zero Trust, businesses can create a robust security framework that adapts to the challenges of today’s interconnected world.